1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
|
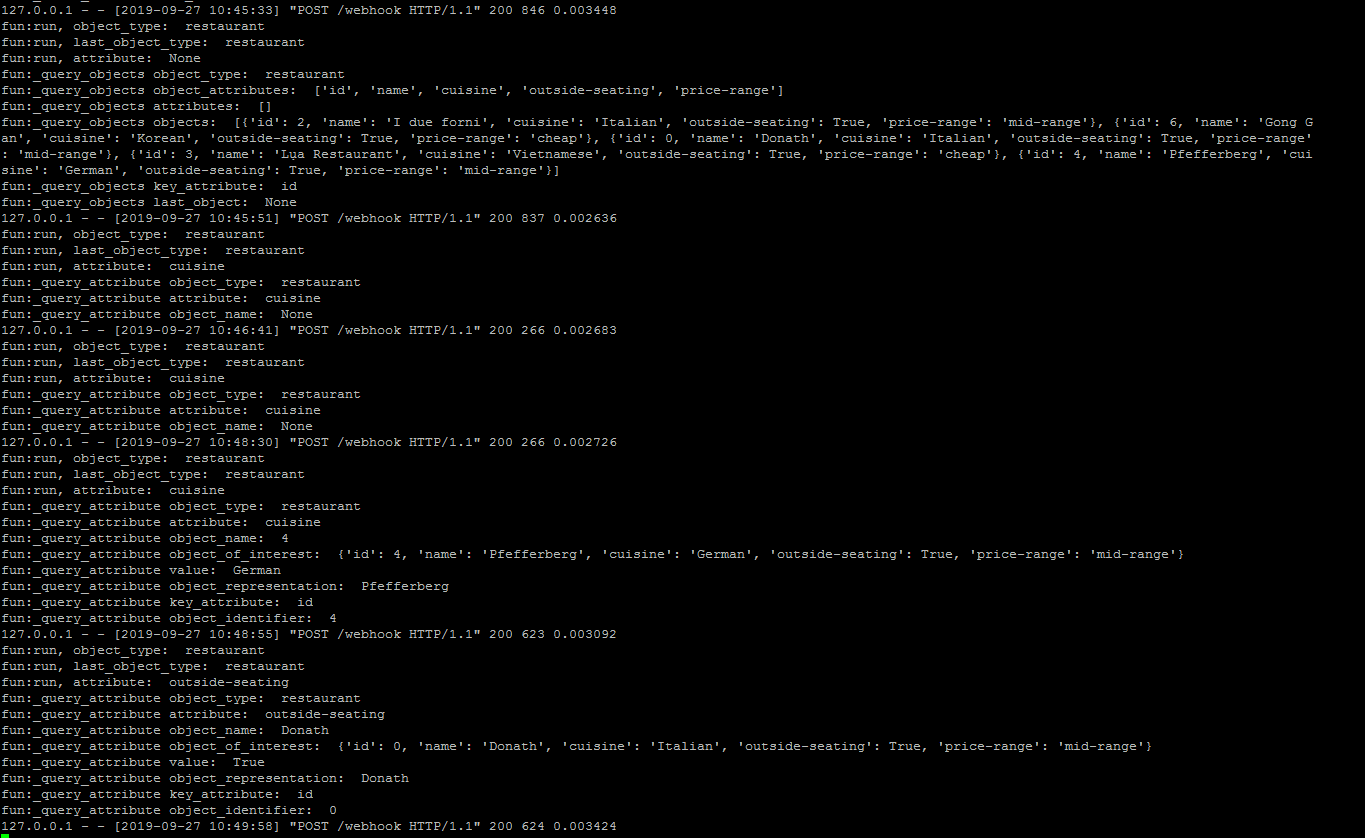
def _query_attribute(self, dispatcher, tracker):
# type: (CollectingDispatcher, Tracker) -> List[Dict]
"""
Queries the knowledge base for the value of the requested attribute of the
mentioned object and outputs it to the user.
Args:
dispatcher: the dispatcher
tracker: the tracker
Returns: list of slots
"""
# 针对:
# list restaurants
# do you know what cuisine the last one has
# 两个问题,当第二个问题处理的时候,进入到这个函数中:
# 此时object_type为restaurants
# attribute为cuisine
object_type = tracker.get_slot(SLOT_OBJECT_TYPE)
attribute = tracker.get_slot(SLOT_ATTRIBUTE)
# 获取用户指代的对象,返回对应的id
object_name = get_object_name(
tracker,
self.knowledge_base.ordinal_mention_mapping,
self.use_last_object_mention,
)
# 笔者添加用来观察变量
print("fun:_query_attribute object_type: ", object_type)
print("fun:_query_attribute attribute: ", attribute)
print("fun:_query_attribute object_name: ", object_name)
if not object_name or not attribute:
dispatcher.utter_template("utter_ask_rephrase", tracker)
return [SlotSet(SLOT_MENTION, None)]
# 根据id和对应的对象类型,获取object
# {'id':2,'name':'I due forni', 'cuisine': 'Italian', 'outside-seating': True, 'price-range': 'mid-range'}
object_of_interest = self.knowledge_base.get_object(object_type, object_name)
print("fun:_query_attribute object_of_interest: ", object_of_interest)
if not object_of_interest or attribute not in object_of_interest:
dispatcher.utter_template("utter_ask_rephrase", tracker)
return [SlotSet(SLOT_MENTION, None)]
# 获取属性对应的值,Italian
value = object_of_interest[attribute]
repr_function = self.knowledge_base.get_representation_function_of_object(
object_type
)
# object_representation = 'I due forni'
object_representation = repr_function(object_of_interest)
key_attribute = self.knowledge_base.get_key_attribute_of_object(object_type)
object_identifier = object_of_interest[key_attribute]
print("fun:_query_attribute value: ", value)
print("fun:_query_attribute object_representation: ", object_representation)
print("fun:_query_attribute key_attribute: ", key_attribute)
print("fun:_query_attribute object_identifier: ", object_identifier)
# 用来给用户反馈消息
self.utter_attribute_value(dispatcher, object_representation, attribute, value)
slots = [
SlotSet(SLOT_OBJECT_TYPE, object_type), # 存储object_type实体值
SlotSet(SLOT_ATTRIBUTE, None), # 将attribute重置None
SlotSet(SLOT_MENTION, None), # 将mention重置为None
SlotSet(SLOT_LAST_OBJECT, object_identifier), # 上一次object的id
SlotSet(SLOT_LAST_OBJECT_TYPE, object_type), # 记录为上一次的object_type实体值
]
return slots
|
![]()